CS:GO Skins Hub
Explore the latest trends and tips on CS:GO skins.
When Your Dinner Turns Deadly: The Unwelcome Guest of Food Poisoning
Discover the shocking truths behind food poisoning and how that meal could become your worst nightmare. Don't let your dinner turn deadly!
Understanding Food Poisoning: What You Need to Know
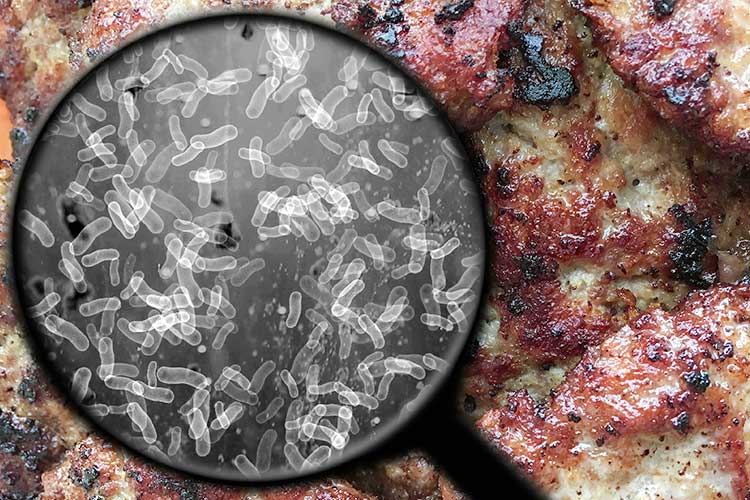
Understanding food poisoning is crucial for maintaining health and safety in the kitchen and dining areas. Food poisoning occurs when microorganisms, such as bacteria, viruses, or parasites, contaminate food. Symptoms often include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal cramps, which can appear within hours or days after consuming contaminated food. To prevent food poisoning, it's essential to practice good food hygiene, which includes washing hands, cooking food to safe temperatures, and storing food properly.
There are several common culprits behind food poisoning, including Salmonella, E. coli, and Listeria. Knowing how these pathogens spread can help you avoid them. Here are some key prevention tips:
- Always wash fruits and vegetables under running water.
- Cook meat to the recommended internal temperatures.
- Avoid cross-contamination by using separate cutting boards for raw meats and produce.
Top 10 Common Foods That Cause Food Poisoning
Food poisoning is a serious health risk that can arise from consuming contaminated food. Some common foods are notorious for harboring harmful bacteria and viruses. This includes raw or undercooked meat, which can often contain pathogens such as Salmonella or E. coli. Shellfish, particularly if sourced from contaminated waters, can also be a vector for foodborne illnesses. In addition, unpasteurized dairy products pose significant risks, as they may contain Listeria or Brucella, which can lead to severe health complications.
Fruits and vegetables are not immune either; leafy greens like spinach and lettuce are frequently linked to outbreaks of food poisoning due to contaminated water supply. Eggs, especially when consumed raw or undercooked, can harbour Salmonella. Rice, particularly if cooked and left at room temperature, is prone to Bacillus cereus growth, leading to gastrointestinal distress. Lastly, processed meats such as hot dogs and deli meats can be contaminated with dangerous bacteria like Listeria if not handled properly.
Is Your Food Safe? How to Prevent Foodborne Illness
Ensuring food safety is crucial in preventing foodborne illness, which can lead to serious health complications. To protect yourself and your family, start by practicing proper hygiene in the kitchen. Always wash your hands with soap and water before handling food, and make sure to keep kitchen surfaces clean. Additionally, make it a habit to separate raw meats from other foods to avoid cross-contamination. Use separate cutting boards for raw meats and fresh produce, and remember to clean utensils thoroughly after each use.
Cooking food at the right temperature is essential in eliminating harmful bacteria that can cause foodborne illness. Use a food thermometer to ensure that meats are cooked to safe internal temperatures—145°F for whole meats, 160°F for ground meats, and 165°F for poultry. Moreover, store perishable items in the refrigerator promptly to prevent spoilage. It is recommended to follow the 2-hour rule: refrigerate leftovers within 2 hours of cooking to keep food safe. By implementing these practices, you can significantly reduce your risk of foodborne illnesses.